Beta Factor Explained: A Complete Guide to Filter Efficiency and Selection
Introduction to the Beta Factor
The importance of the Beta Factor for filtration technology is well known. Industrial machinery, hydraulic systems, and other filtration applications. Whether you are running industrial machinery, hydraulic systems, or other previous filtration applications, being in the know about the Beta Factor will enable you to make informed decisions on how to select a filter. This article will take a close look at what the Beta Factor is, why it is important, and how it can be used properly to maintain efficient, sustainable systems.
What is the Beta Ratio?
The Beta Ratio, or the Beta Factor, is an expression of how well a filter will remove particles of a particular size. It is a measure of the filtration of contaminants out of a fluid. The Beta Ratio is established using the internationally recognized ISO 16889:1999 multi-pass test standard, which is the internationally acknowledged procedure used to determine filter performance.
Importance of Beta Ratios in Filtration
Selecting a filter with the right Beta Ratio is necessary for keeping fluid systems clean and operating in the most productive manner. Poor filtration can lead to:
- More wear and tear on the lessee's machinery
- Reduced operational efficiency
- Higher maintenance costs
- Risk of equipment failure
High Beta Ratio filters contribute to risk reduction by removing particles from fuel and protecting system reliability and performance.
How is the Beta Ratio Measured?
The Beta Ratio is determined by a test procedure: Transmission testing is conducted in a controlled environment.
- Test Setup: Known-sized particles are added to a test fluid until saturation is obtained.
- Filtrate: The fluid passing through the filter.
- Measurement: Particle counts in the fluid (upstream / before filtration and downstream / after filtration).
- Calculation:Beta Ratio is calculated from the following formula:
Beta Ratio = Number of upstream particles / Number of downstream particles
For example, if a 5 micron filter had 100 upstream particles and 10 downstream particles, the Beta Ratio would be 10.
For More Information - Click Here

Decoding the Beta Factor Formula
To better understand the Beta Factor, let’s break it down:
- (Beta Factor): Represents the particle size (“x” microns) for which the ratio is calculated.
- Efficiency (%): The filter’s efficiency can be derived from the Beta Ratio using the formula:
For example:
Each Beta factor corresponds to an efficiency of the filter, the same can be matched as per the below chart.
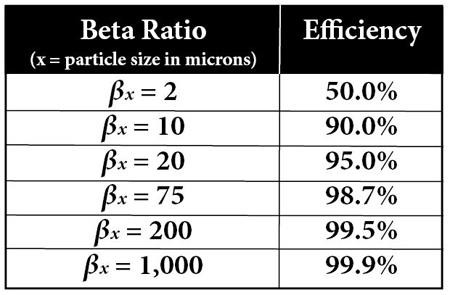
Efficiency and Performance: Understanding Beta Ratings
High Beta Ratios result in more efficient particle filtering. Well, here is a helpful guide:
| Beta Ratio (\u03b2x) | Efficiency (%) | Quality of Filtration |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 50 | Poor |
| 10 | 90 | Moderate |
| 75 | 98.7 | High |
| 200 | 99.5 | Very High |
| 2000 | 99.95 | Excellent |
Choosing the Right Filter Based on Beta Ratios
While choosing a filter, you need to keep in mind the following:
- Application Considerations: Determine the cleanliness level required for your system.
- Particle Size:Check that the filter captures the size of particles you are concerned about.
- Beta Ratio:Select filters with a higher Beta Ratio for critical systems.
- Manufacturer’s Specifications: Use in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions to achieve the best results.
Advantages Of Using a High Beta Ratio Filter
There are several benefits of investing in high-grade filters with better Beta Ratios:
- Extended equipment life
- Less maintenance and downtime
- Enhanced system performance
- Lower operational costs
- Better safety and performance
Common Misconceptions About Beta Ratios
- The higher the Beta Ratio, the better: The higher the Beta Ratio, the better a filter will perform, but the highest Beta Ratio is not always necessary. Over-specification can increase costs without generating a substantial increment in value.
- Beta Ratios Are Universal: Beta Ratios are particle-size-biased. The efficiency of a filter at 5μm is not necessarily indicative of its efficiency at 10 μm.
- You Can Measure It Once: Beta Ratios need to be measured periodically to factor in filter wear and system modifications.
Conclusion
The Beta Factor forms the basis of all efficient filtration technology, allowing the efficiency of a filter in removing contaminants to be measured. Now that you understand the Beta Ratio, you can start making educated decisions on filter selection, allowing you to run your system at the highest level of cleanliness, reliability, and efficiency. Although higher Beta Ratios often equate to finer filtration, choosing the proper filter should be done by considering application requirements, particle sizes, and economics. With this information, you can optimize system performance, prolong equipment life, minimize maintenance costs, and get more out of your operations.
Learn more about our services and industry insights by visiting our official LinkedIn page: Minimac Systems