What is a Compressor? Types, Functions, Technology, and Applications
Introduction
A compressor is a device that increases the pressure of a gas by decreasing its volume. It is an important working fluid in many industrial applications because of its low cost, its non-toxic and non-flammable nature, and its high thermodynamic efficiency. Knowing what a compressor is, various compressor types, what is functioning of the compressor?, what the technology behind the compressor is, and what the applications of the Compressor is very important while selecting a compressor for the particular applications.
The compressors are used in most industries like manufacturing, oil and gas, automotive, HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning), construction, and medical sectors. Providing compressed air or gas is something that a compressor can supply, which has an important role in many contemporary mechanical and industrial systems.
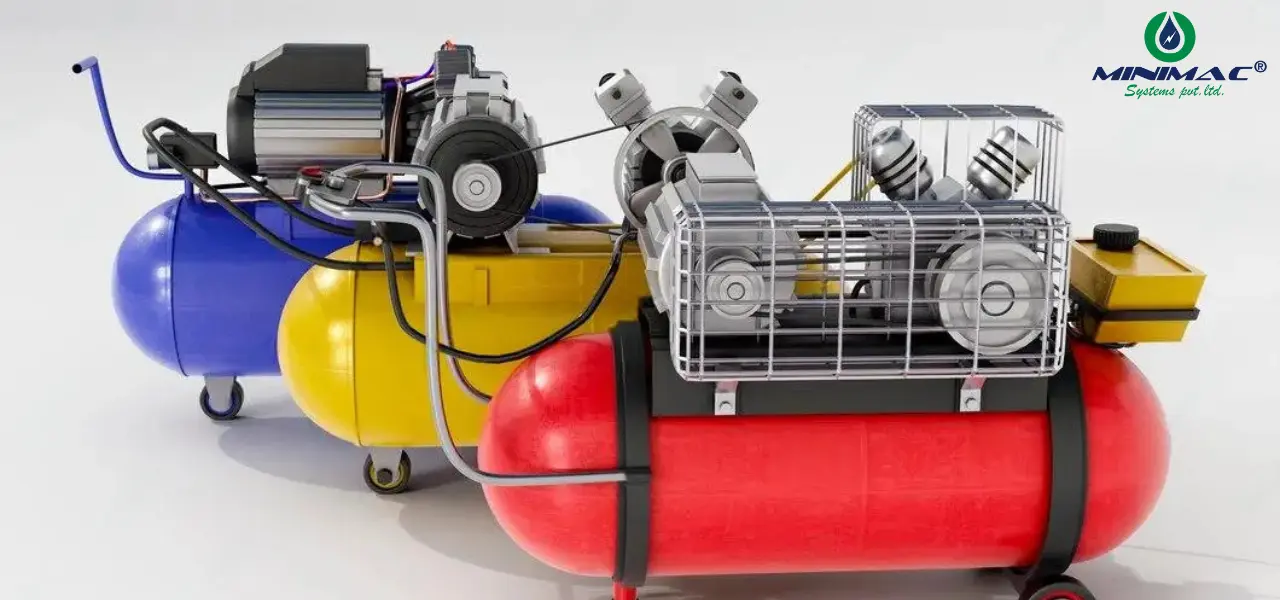
What is a Compressor?
A compressor is defined as a machine used to compress gases to a higher pressure level. The process would draw a gas into a chamber, then decrease its volume and expel the gas at a higher pressure. Compressor machines are essentially equipment that they used in pneumatics, HVAC technology, industrial machinery work, and petrol or liquefied gas trucks.
The functioning of a compressor depends on thermodynamics and fluid mechanics. The compressor works on gas mechanically, which causes to rise its pressure and a decrease in volume. The various types of compressors use a variety of means to efficiently compress the gas.
Types of Compressors
Compressors may be categorized into two general types: positive displacement and dynamic.
Compressors of Positive Displacement
These compressors operate by holding gas and then decreasing its volume to raise pressure.
The main types include:
- Reciprocating Compressor:Compresses gas by using a piston to reciprocate in a cylinder, widely used in small-to-medium industrial plants. They are extensively used in gas transmission and refrigeration.
- Piston Compressor:A particular reciprocating compressor that uses one or more cylinders that make it move backward and forward. It is widely used in automotive and industrial applications.
- Reciprocating Piston Compressor:A technical term used for compressors reciprocating with piston-based mechanisms.
- Reciprocating Piston Compressor / Reciprocating CompressorA technical term for Compressors that are operated with pistons.
- Piston Air Compressor: Used in air compression for industrial, medical, or automotive uses.
- Rotary Screw Compressor: This type of compressor is widely popular for its ability to compress gas with utmost efficiency, particularly useful for projects involving continuous operation, requiring large volumes of gas.
- Scroll Compressor:Consists of interleaving scrolls to compress gas, typically used in an HVAC system or refrigeration.
Dynamic Compressors
These compressors work by spinning blades at a very high speed, thereby giving the gas a high speed that will become pressure. The main types include:
- Centrifugal Compressor: A centrifugal compressor has a radial design (analogous to the design of a water wheel) and extracts energy from the flow by using centrifugal forces on the gas molecule.
- Axial Compressor: Jet engines and other gas turbines, requiring high power and good efficiency and where a continuous flow is needed to compress the Gas. It is intended for high speed, the aerospace industry is a big user.
Compressor Functions
- The compressor works rely upon the type and the use of the work. Key roles include:
- Raising the pressure of gas for industrial and commercial use.
- Compressed air for pneumatic tools, in both Industrial applications, such as manufacturing and construction.
- Facilitating cooling for air conditioning and refrigeration systems.
- Propulsion of engines in cars and planes to make them burn cleaner and more efficiently.
- It is used to assist the transmission of gas in pipelines of the oil and gas industry.
- Providing breathable air to medical and diving applications, etc.
Every type of compressor is designed for a specific use based upon its working principle and the industry in which it is used. Knowing these functions is important as it will allow the selection of the appropriate type of compressor for a specific application.
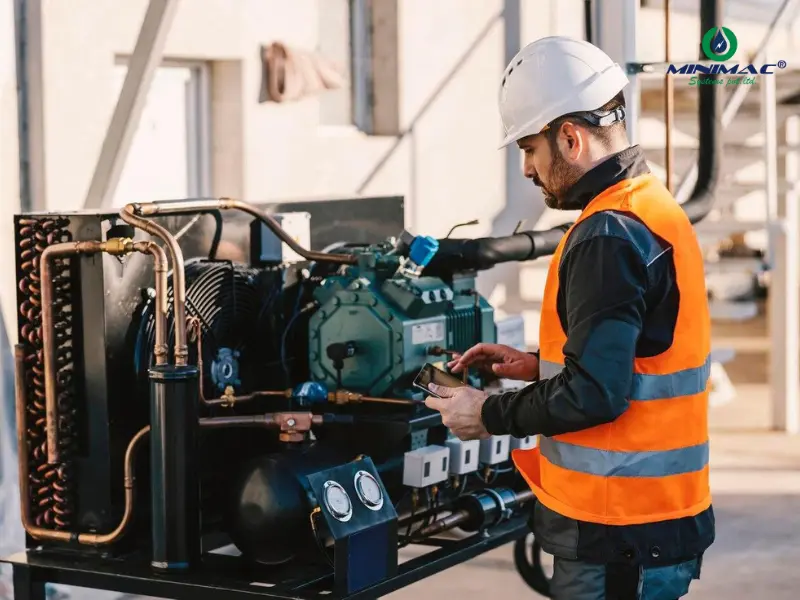

Compressor Technology
Recent progress of compressor technology with higher efficiency, energy saving, lower noise, etc. Key innovations include:
- VSD Compressors:Alter motor speed according to demand – saving energy. These compressors assist industries in bringing down their electricity bills and enhancing efficiency.
- Oil-Free Compressors:Perfect for processes requiring 100% oil-free air, such as pharmaceuticals and food processing. They supply fresher air to the engine with oil-free lubrication.
- Smart Compressor Systems:Leveraging IOT for Predictive Maintenance and Performance Optimization. Such smart devices enhance operational reliability by predicting failures in advance.
- ENERGY SAVING COMPRESSORS:Designed to consume minimum power, leading to low operational cost, thereby cost and energy -and energy-efficient.PRODUCT These days, modern compressors are often built with heat recovery and enhanced sealing technology.
- HP series compressors: purpose-built to survive in extreme pressure applications, for industrial applications only. These are often used in gas pipelines, chemical plants and hydraulic systems.
Compressor Applications
Due to their versatility, compressors are utilized in various businesses. The compressor is commonly used in the following applications:
- Industrial Applications: Compressors run the machines in factories, doing everything from painting to running assembly lines.
- Automotive: In vehicle air conditioning, braking and turbocharging for increased performance.
- HVAC Systems: Compressors: control the temperature of an air conditioning system, designed to cool and dehumidify.
- Medical Industry: Supply clean compressed air for ventilators, dental apparatus, and laboratories.
- Oil & Gas:Support in gas process, refinery and fuel distribution through pipeline transmission.
- Construction and Mining:Operating heavy machinery, jumpers, and drilling tools on job sites.
For More Information about oil filtration,Click Here.
Compressor Maintenance and Fault Finding:
Comprehensive care provides long-term whole-life efficiency and cost savings, as well as reduced commissioning time, increased reliability, and minimized downtime for the compressor. Such repairs would be: lubrication, cleaning of filters, leak inspection, and inspection of vibration.
A Few of the Key Points to Keeping Your Compressors Running Trouble Free
Compressors are one of the most important elements in industrial applications:
making it possible to achieve a constant supply of compressed air for various use cases. Maintenance on a consistent basis can improve performance, decrease breakdowns and lengthen the life of the equipment. Here are some key maintenance points for compressors, explained in further detail:
Air Filter Maintenance
The air filter keeps dust, dirt, and impurities from contaminating the compressor. Blocked/dirty air filters make your system work harder, resulting in higher energy bills and potential damage to your furnace. It is also advisable to check on a weekly basis and to clean or replace it every 1000 hours of use, or when working in a dusty ambient.
Oil Filter Maintenance
The lubricating oil is purified by means of the oil filter. Clean oil is necessary to protect against wear and move parts in sequence. Dirty oil filters result in oil contamination that makes for wear, overheating and lower efficiency. Weekly changing and replacement as required (1000 hours) keeps your wastewater flowing smoothly.
Lubricant Management
As you may know, oil is used for lubricating, that is, making sure the internal parts of the compressor can move with little or no friction. Lube can break down, get stuff in it, and/or get "thinner." Oil levels and oil quality should be checked daily. Full oil change every 4000-8000 hours, depending on lubricant quality, operating conditions and manufacturer guidelines.
Separator Element Maintenance
The separator is responsible for separating oil from compressed air so that the compressor delivers clean, contamination-free air to the system. A stretched-out or oil-saturated separator will cause the oil carryover to be higher and will cause higher oil consumption, lower quality air, and system contamination. The separator should be checked weekly and changed at each lubricant change.
Motor Bearing Lubrication
Motor bearings are essential for the proper rotation of the compressor motor. Without adequate lubrication, bearings can and will wear out prematurely, turning into an open flame, taking mount at overdoing (and even motor) failure. Frequent examination, weekly or every 500 hours, saving time and getting bearings in great working order, and re-greening as much as 2000 hours (or as required).
Check and Adjust Drive Belt
The power from the motor is transmitted by the belts to the compressor unit. Belts can stretch and wear out over time. Slip-and-worn belts lower productivity and they can even break suddenly, leading to downtime. Weekly checking, adjusting of tension and replacement of worn belts will maintain proper operation.
Intake Vent Cleaning
Admission Vent: the vent provides the compressor suck in cool air. Blocked up vents create air resistance and put a strain on the compressor, which ends up using more electricity. If you do weekly visual inspections of the intake vents and keep them clean, the compressor won’t have to work as hard and your unit will be more efficient.
A comprehensive and well-planned maintenance program is necessary for any industrial compressor. By following these recommendations, it will help prevent unscheduled compressor failures, minimize repair costs and keep the drive running at peak efficiency for years. Always consult the manufacturer's manual for equipment-specific maintenance requirements and maintain a record of scheduled maintenance.
Conclusion
To choose the appropriate equipment, you need to know what a compressor is, the types of compressors, the purpose or function of compressors, compressor technology and compressor application. And now with a broad range of applications in industries such as manufacturing, automotive, HVAC, and healthcare, compressors are as relevant as ever to industry, technology and its efficiency.
Learn more about our services and industry insights by visiting our official LinkedIn page: Minimac Systems on LinkedIn





